Median and Achaemenid Empire (650 BC–330 BC)
Main articles: Median Empire and Achaemenid Empire
The Immortal Soldiers at Darius' palace at Susa. |
After his father's death in 559 BC, Cyrus the Great became king of Anshan but like his predecessors, Cyrus had to recognize Mede overlordship. In 552 BC Cyrus led his armies against the Medes and captured Ecbatana in 549 BC, effectively conquering the Median Empire and also inheriting Assyria. Cyrus later conquered Lydia and Babylon. Cyrus the Great created the Cyrus Cylinder, considered to be the first declaration of human rights and was the first king whose name has the suffix "Great". After Cyrus' death, his son Cambyses ruled for seven years (531-522 BC) and continued his father's work of conquest, making significant gains in Egypt. A power struggle followed Cambyses' death and, despite his tenuous connection to the royal line, Darius was declared king (ruled 522-486 BC).
Darius' first capital was at Susa, and he started the building programme at Persepolis. He rebuilt a canal between the Nile and the Red Sea, a forerunner of the modern Suez Canal. He improved the extensive road system, and it is during his reign that mention is first made of the Royal Road (shown on map), a great highway stretching all the way from Susa to Sardis with posting stations at regular intervals. Major reforms took place under Darius. Coinage, in the form of the daric (gold coin) and the shekel (silver coin) was introduced (coinage had already been invented over a century before in Lydia ca. 660 BC),[26] and administrative efficiency was increased. The Old Persian language appears in royal inscriptions, written in a specially adapted version of cuneiform. Under Cyrus the Great and Darius the Great, the Persian Empire eventually became the largest empire in human history up until that point, ruling and administrating over most of the then known world.[27] Their greatest achievement was the empire itself. The Persian Empire represented the world's first superpower.[1][28] that was based on a model of tolerance and respect for other cultures and religions.[29]
In 499 BC Athens lent support to a revolt in Miletus which resulted in the sacking of Sardis. This led to an Achaemenid campaign against Greece known as the Greco-Persian Wars which lasted the first half of the 5th century BC. During the Greco-Persian wars Persia made some major advantages and razed Athens in 480 BC, but after a string of Greek victories the Persians were forced to withdraw while losing control of Macedonia, Thrace and Ionia. Fighting ended with the peace of Callias in 449 BC. In 404 BC following the death of Darius II Egypt rebelled under Amyrtaeus. Later Egyptian Pharaohs successfully resisted Persian attempts to reconquer Egypt until 343 BC when Egypt was reconquered by Artaxerxes III.
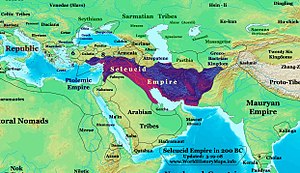
The Hellenic conquest and the Seleucid Empire (312 BCE – 63 BCE)
Main article: Seleucid Empire
In 334 BC-331 BC Alexander the Great, also known in the Zoroastrian Arda Wiraz Nâmag as "the accursed Alexander", defeated Darius III in the battles of Granicus, Issus and Gaugamela, swiftly conquering the Persian Empire by 331 BC. Alexander's empire broke up shortly after his death, and Alexander's general, Seleucus I Nicator, tried to take control of Persia, Mesopotamia, and later Syria and Asia Minor. His ruling family is known as the Seleucid Dynasty. However he was killed in 281 BC by Ptolemy Keraunos. Greek language, philosophy, and art came with the colonists. During the Seleucid Dynasty throughout Alexander's former empire, Greek became the common tongue of diplomacy and literature. Overland trade brought about some fascinating cultural exchanges. Buddhism came in from India, while Zoroastrianism travelled west to influence Judaism. Incredible statues of the Buddha in classical Greek styles have been found in Persia and Afghanistan, illustrating the mix of cultures that occurred around this time (See Greco-Buddhism).Parthian Empire (248 BC – 224 AD)
Main article: Parthian Empire
Parthia was led by the Arsacid dynasty, who reunited and ruled over the Iranian plateau, after defeating the Greek Seleucid Empire, beginning in the late 3rd century BC, and intermittently controlled Mesopotamia between ca 150 BC and 224 AD. It was the second native dynasty of ancient Iran (Persia). Parthia was the Eastern arch-enemy of the Roman Empire; and it limited Rome's expansion beyond Cappadocia (central Anatolia). The Parthian armies included two types of cavalry: the heavily armed and armoured cataphracts and lightly armed but highly mobile mounted archers. For the Romans, who relied on heavy infantry, the Parthians were too hard to defeat, as both types of cavalry were much faster and more mobile than foot soldiers. On the other hand, the Parthians found it difficult to occupy conquered areas as they were unskilled in siege warfare. Because of these weaknesses, neither the Romans nor the Parthians were able to completely annex each other.
The Parthian empire lasted five centuries, longer than most Eastern Empires. The end of this long lasted empire came in 224 AD, when the empire was loosely organized and the last king was defeated by one of the empire's vassals, the Persians of the Sassanian dynasty.
Sassanid Empire (224 – 651 AD)
Main article: Sassanid Empire
The first Shah of the Sassanid Empire, Ardashir I, started reforming the country both economically and militarily. The empire's territory encompassed all of today's Iran, Iraq, Armenia, Afghanistan, eastern parts of Turkey, and parts of Syria, Pakistan, Caucasia, Central Asia, India and Arabia. During Khosrau II's rule in 590-628, Egypt, Jordan, Palestine and Lebanon were also annexed to the Empire. The Sassanians called their empire Erânshahr (or Iranshahr, "Dominion of the Aryans", i.e. of Iranians).[30] Rock-face relief at Naqsh-e Rustam of Iranian emperor Shapur I (on horseback) capturing Roman emperor Valerian I (kneeing) and Philip the Arab (standing) .
Rock-face relief at Naqsh-e Rustam of Iranian emperor Shapur I (on horseback) capturing Roman emperor Valerian I (kneeing) and Philip the Arab (standing) .The Sassanian era, encompassing the length of the Late Antiquity period, is considered to be one of the most important and influential historical periods in Iran, and had a major impact on the world. In many ways the Sassanian period witnessed the highest achievement of Persian civilization, and constitutes the last great Iranian Empire before the adoption of Islam. Persia influenced Roman civilization considerably during Sassanian times,[31] their cultural influence extending far beyond the empire's territorial borders, reaching as far as Western Europe,[32] Africa,[33] China and India[34] and also playing a prominent role in the formation of both European and Asiatic medieval art.[35] This influence carried forward to the Islamic world. The dynasty's unique and aristocratic culture transformed the Islamic conquest and destruction of Iran into a Persian Renaissance.[32] Much of what later became known as Islamic culture, architecture, writing and other contributions to civilization, were taken from the Sassanian Persians into the broader Muslim world